What Is Hypertension? Causes, Symptoms & Risks
Discover what hypertension is, its common causes, symptoms, and risk factors. Learn how high blood pressure affects health and why early detection matters. Informational guide for better understanding.
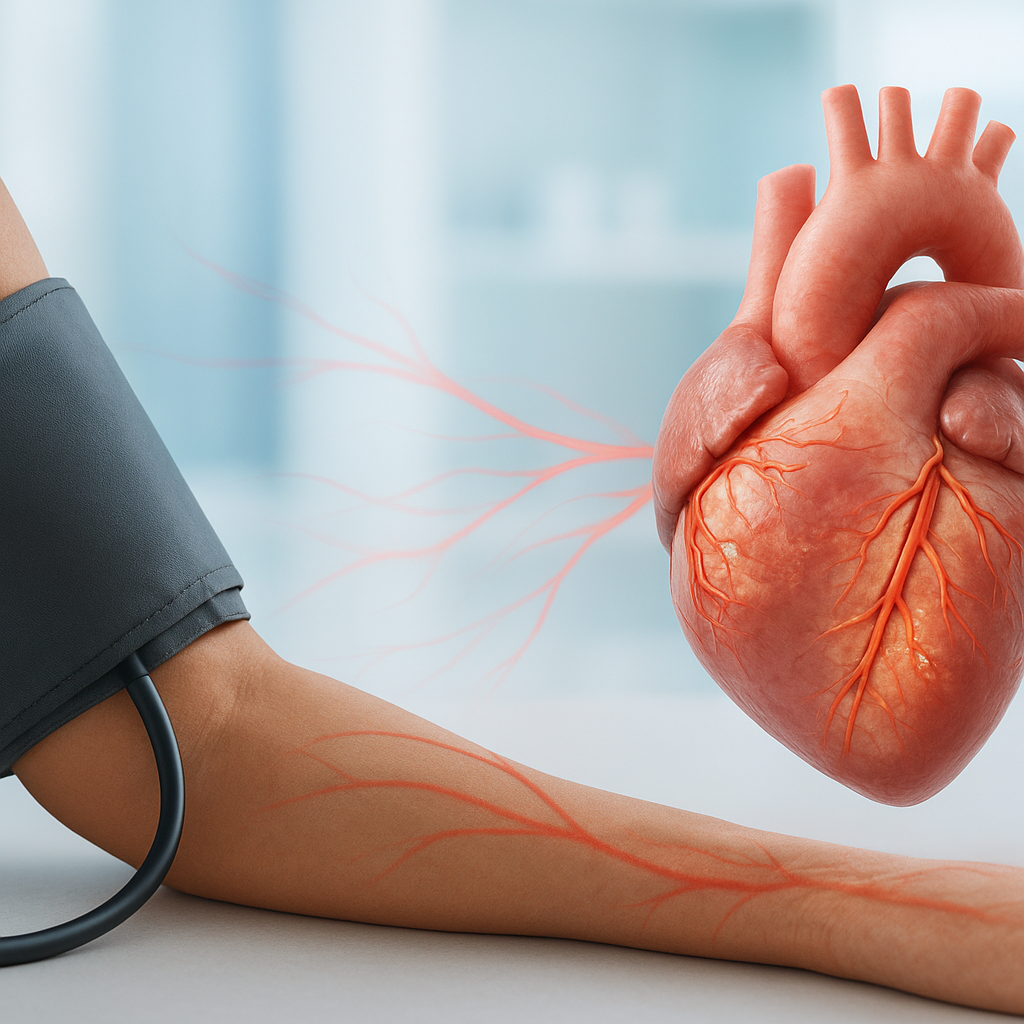
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a condition where the force of blood against artery walls is consistently too high. It often has no symptoms, earning it the nickname 'silent killer,' and affects millions worldwide. Understanding hypertension is crucial for maintaining heart health and preventing complications like heart disease and stroke.
Defining Hypertension and Blood Pressure Basics
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and recorded as two numbers: systolic (top number) over diastolic (bottom number). Normal blood pressure is below 120/80 mmHg. Hypertension is diagnosed when readings are consistently 130/80 mmHg or higher. Primary hypertension develops gradually over years, while secondary hypertension arises from underlying conditions.
Common Causes of Hypertension
Most cases of hypertension are primary, linked to genetics, aging, and lifestyle factors. Secondary hypertension, about 5-10% of cases, stems from issues like kidney disease or hormonal disorders. Key contributors include excessive salt intake, lack of physical activity, and obesity.
Dietary factors: High sodium diets cause fluid retention, raising pressure.
Lifestyle habits: Smoking damages blood vessels; stress triggers hormone release.
Medical conditions: Sleep apnea or thyroid problems can elevate readings.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Hypertension is often asymptomatic, but severe cases may show headaches, shortness of breath, or nosebleeds. Long-term effects include vision problems or chest pain. Regular monitoring is essential since symptoms appear only in advanced stages.
Headaches: Especially in the morning, linked to high pressure.
Fatigue and confusion: Due to reduced blood flow to the brain.
Irregular heartbeat: Can signal hypertensive heart strain.
Risk Factors and Complications
Certain factors increase hypertension risk, such as family history, age over 65, and being overweight. African Americans face higher prevalence. Untreated, it leads to heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, and aneurysms.
Age and genetics: Risk rises with age; family history plays a role.
Obesity and inactivity: Excess weight strains the heart.
Examples: In the U.S., over 116 million adults have hypertension; globally, 1.28 billion people aged 30-79.
Diagnosis and Prevention Strategies
Diagnosis involves multiple blood pressure readings, possibly with home monitors or ambulatory devices. Prevention focuses on lifestyle: balanced diet, exercise, and weight management. Routine check-ups help catch it early.
Real-world examples include the DASH diet, proven to lower pressure, and programs like the WHO's global hypertension initiative targeting awareness in low-resource areas.